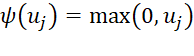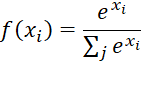BC/NW 2024 ¹ 1 (41):13.2
ENHANCING BIOMETRIC AUTHENTICATION THROUGH THE APPLICATION OF RELU AND MULTILAYER PERCEPTRONS IN MOUSE MOVEMENT ANALYSIS
Óéìèí À.Ã., Áåëîóñîâ À.Â.
This paper presents the findings of a pioneering study focused on the development of a biometric authentication algorithm leveraging the dynamics of mouse movements. The core methodology integrates Rectified Linear Units (ReLU) and multilayer perceptrons, components of neural network architecture, to analyze and interpret the intricacies of mouse motion [1], [2].
In
our approach, each neuron's output in a given layer (denoted as ![]() for the
for the ![]() neuron in layer
neuron in layer ![]() ) is computed as a weighted
sum of its inputs, followed by a non-linear activation function—specifically
ReLU for hidden layers. This is mathematically represented by the ReLU function
(1) which introduces non-linearity to the learning process, essential for
capturing complex patterns.
) is computed as a weighted
sum of its inputs, followed by a non-linear activation function—specifically
ReLU for hidden layers. This is mathematically represented by the ReLU function
(1) which introduces non-linearity to the learning process, essential for
capturing complex patterns.
|
|
(1) |
The
network consists of two layers. The transformation from inputs to outputs
within the network is structured through the application of weighted sums
followed by the activation function, where the weight matrix ![]() represents the synaptic weights between layer
represents the synaptic weights between layer 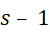 and layer
and layer![]() .
.
The softmax function (2) is employed at the output layer to convert the logits into a probability distribution over the predicted classes [3].
|
|
(2) |
The research demonstrates that the utilization of ReLU activation functions within multilayer perceptrons significantly improves the algorithm's ability to distinguish between individual users based on their unique mouse movement patterns, processed through a softmax layer for accurate probability representation. Key findings indicate that this method not only enhances the accuracy of user authentication but also introduces a level of robustness against common spoofing attempts.
Ëèòåðàòóðà
1. Asadi B., Jiang H. On approximation capabilities of ReLU activation and softmax output layer in neural networks //arXiv preprint arXiv:2002.04060. – 2020.
2. Chong P., Elovici Y., Binder A. User authentication based on mouse dynamics using deep neural networks: A comprehensive study //IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security. – 2019. – Ò. 15. – Ñ. 1086-1101.
3. Shen K. et al. A Study on ReLU and Softmax in Transformer //arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.06461. – 2023.