RESEARCH OF WIDE AREA NETWORKS
PERFORMANCE
L.I.Abrosimov,
K.V. Sultanov, Maishan Sedaghati
(Moscow, Russia Moscow Power Engineering Institute (Technical University))
The computer network is a technical system containing computers,
connected by communication devices and channels of communication, which
provides remote performance of information tasks of the users.
The productivity or performance of computer
network as a system serving users, should be estimated by the total number of information tasks,
which are carried out by all devices included into the structure of computer
network.
Computer networks carry out functions of
transferring and data processing and carry out transformation of the requests
to the messages and vice versa. Because the
requests and messages are functionally related to each other, in
notation we shall use the term transaction,
which is defined by two parameters: the
volume of the data and the number of computing operations necessary for
processing.
Because of different requirements and the
use of various degrees of decomposition
at the description of processing transactions in computer networks, it is
necessary to use several degrees of computer networks
performance, which first of all it is
possible to arrange the concepts of computer networks performance as following:
- Computer
network performance of elements,
- Computer
network performance of nodes,
- Complex
computer network performance,
- Working
computer network performance,
- Peak
computer network performance,
- Limiting
of computer network performance for considered type of transactions at peak
loading.
In the
basis of the method of calculation of
computer network performance the method of contours is taken place [4], [5].
In the
report the example of calculation of WAN
performance with application of the
developed methods is in detail considered.
The given
WAN, submitted in figure 1, contains in its structure: servers 1H - 5H (in the
model are substituted numbers 1-5), switching controllers 1 - 10, connected
communication channels, (numbers 6-27)
and group of the subscribers 1G - 5G (numbers 28-31, 32-37, 38-45, 46 51,
52-57) .

Figure 1- Given WAN structure
The subscribers 1G - 5G in a dialogue mode
interacts with appropriate servers in the scheme:
1G-1H (contour q=1); 2G-5H (q=2); 3G-1H (q=3); 4G-1H
(q=4); 5G-2H (q=5).
In the given WAN the initial variant of routes for all
of contours was set by a principle " fixed (uniform)loading of
communication channels ".
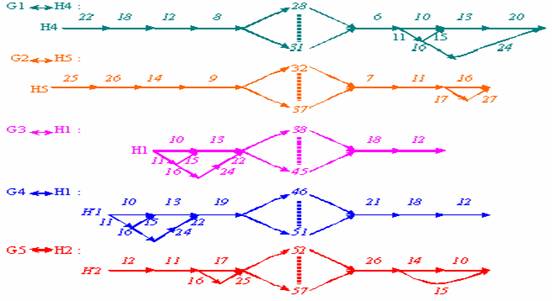
Figure 2. Diagram of contours in a given WAN
In the following example
the values of service intensity are accepted:
![]() 6 1/с;
6 1/с; ![]() 4 1/с ;
4 1/с ; ![]() 0,333 1/с.
0,333 1/с.
According to the previous definitions, we
can get the following numerical values
for the given WAN performance.
·
The
WAN performance of MN nodes,
in our example does not depend on contours and can be written as following :
![]() 1/с . The
values MN are used as the initial data for the further calculations.
1/с . The
values MN are used as the initial data for the further calculations.
· Complex
МС WAN performance is written in a line for
each contour q and in our example for q=1 it is possible to write as following :
![]() 1/с .МС
allows to calculate the minimal time of delivery transactions for each contour
q.
1/с .МС
allows to calculate the minimal time of delivery transactions for each contour
q.
·
Working
WAN performance is determined at ![]() and for our example:
and for our example:
{NWq}
={2,3,4,3,3}, NQ = 5, {![]() } = {0,171; 0,179; 0,248; 0,225; 0,184} 1/c,
} = {0,171; 0,179; 0,248; 0,225; 0,184} 1/c, ![]() =3,0991/c; {tWq} = {2,84;
2,595; 2,366; 2,916; 2,436} с
=3,0991/c; {tWq} = {2,84;
2,595; 2,366; 2,916; 2,436} с
·
Peak WAN
performance, is determined at ![]() and for our example: {NPq}={4,6,8,6,6},
NQ = 5, {
and for our example: {NPq}={4,6,8,6,6},
NQ = 5, {![]() } = {0,136; 0,150; 0,190; 0,175; 0,139} 1/c,
} = {0,136; 0,150; 0,190; 0,175; 0,139} 1/c, ![]() = 4,8461/c; {tPq} =
{4,353; 3,667; 4,02; 4,634; 4,171} с
= 4,8461/c; {tPq} =
{4,353; 3,667; 4,02; 4,634; 4,171} с
·
limiting
of WAN performance at limiting time of reaction of system ![]() =7,2 с.
=7,2 с.
For our example : {NLq}
={6,9,12,9,9}, NQ = 5, {![]() } = {0,1056; 0,120; 0,140; 0,131; 0,1} 1/c,
} = {0,1056; 0,120; 0,140; 0,131; 0,1} 1/c, ![]() = 5,469 1/c ;{tLq}
= {6,456; 5,361; 6,511; 7,165; 7,028} с .
= 5,469 1/c ;{tLq}
= {6,456; 5,361; 6,511; 7,165; 7,028} с .
|
|
|
|
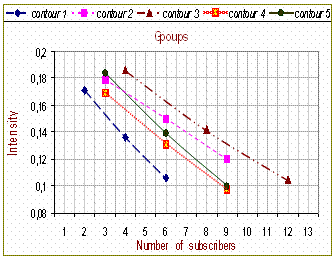
Figure 3. Shows the
intensity of transactions being serviced in different contours from the
respective number of subscribers |
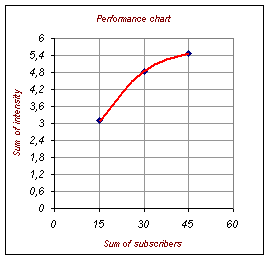
Figure 4. Shows the total of
the WAN performance depend on the number of subscribers (working WAN
performance, peak performance and limiting performance).
|
Subscribers in the given WAN (wide area
networking ) use dialogue interactions with servers, therefore the
following functioning modes: working,
peak and limiting depend on the number of active subscribers .
In the Working mode {NWq}
={2,3,4,3,3}, means. 15 Subscribers
In the Peak mode {NPq}
={4,6,8,6,6}, means. 30 Subscribers
In the limiting mode {NLq}
={6,9,12,9,9}, means. 45 Subscribers
The increase of the number
of subscribers (from the point of view of subscribers) reduces the performance
of the network (see figure 3) as it increases the number of transactions in the
network and the line also increases ,in the same way an increase
in number of subscribers (from the systems administrator’s point of view )
increases the sum performance of the network (see figure 4)
The
conclusion
The offered method of
calculation of WAN performance allows:
- To give the developers and
system administrators an opportunity to estimate quantitatively functioning computer network performance;
- To have a quantitative
estimation for various variants of organization of computer network during
development and modernization computer network;
- To determine
"bootlenec" places in computer network and to offer the proved
solutions based on their elimination by providing of additional resources or
realization of reconfiguration computer network .
References
[1] Методы
автоматизированного проектирования систем телеобработки данных// Учеб. пособие
для вузов/ В.А. Мясников, Ю.Н. Мельников, Л.И. Абросимов. - М.:
Энергоатомиздат,- 1992. - 288 с.: ил.
[2] Абросимов Л.И. Основные
положения теории производительности вычислительных сетей / Вестник МЭИ – 2001 -
№4 – С 70 - 75
[3] Abrosimov L.I.
Conception of creation of intelligent integrated management platform for
heterogeneous computer networks on the basis of tensortransform modeling.
International Conference DISTRIBUTED COMPUTER COMMUNICATION NETWORKS. Theory
and Applications 4 - 8.11.1997 Tel-Aviv (Israel). Institute for Information
Transmission Problems RAS, Tel-Aviv Universiti, M:. 1997 s.3 - 11.
[4] Абросимов Л.И. Анализ и
проектирование вычислительных сетей: Учебное пособие - М.:, Изд-во МЭИ. 2000. -
52 с
[5] Lehr- und Uebungsbuch Telematik /Hrsg. Gerhard Kruger ; Dietrich
Reschke. Autoren Leonid I. Abrosimov, Jorg Deutschmann, Werner Horn, Holger
Reif, Dietrich Reschke, Jochen Schiller, Jochen Seitz. Muenchen;
Wien:Fachbucherverl. Leipzig im Carl-Hanser-Verl., 2000.S 85-98(412 s)